- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
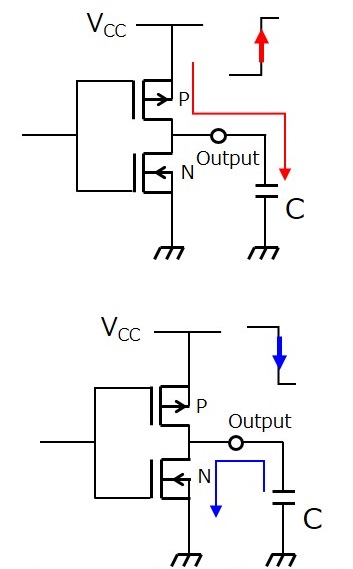
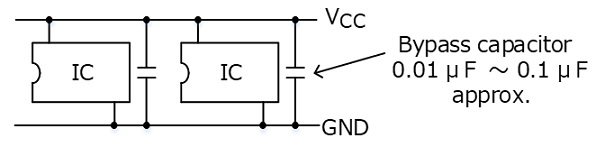
将负载电容连接到CMOS输出引脚
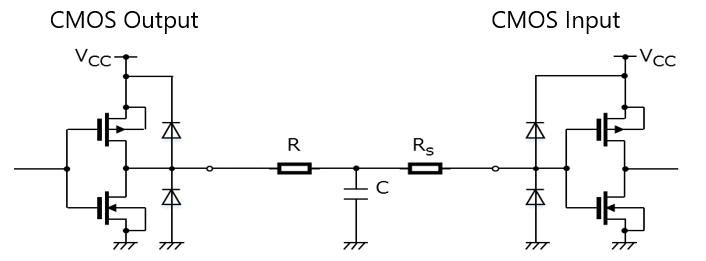
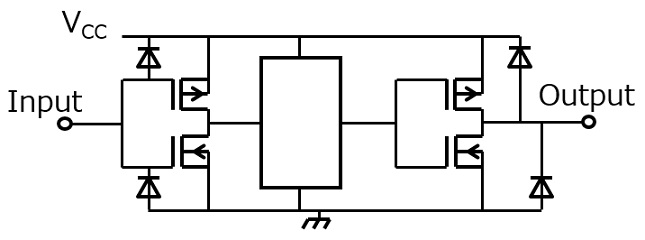
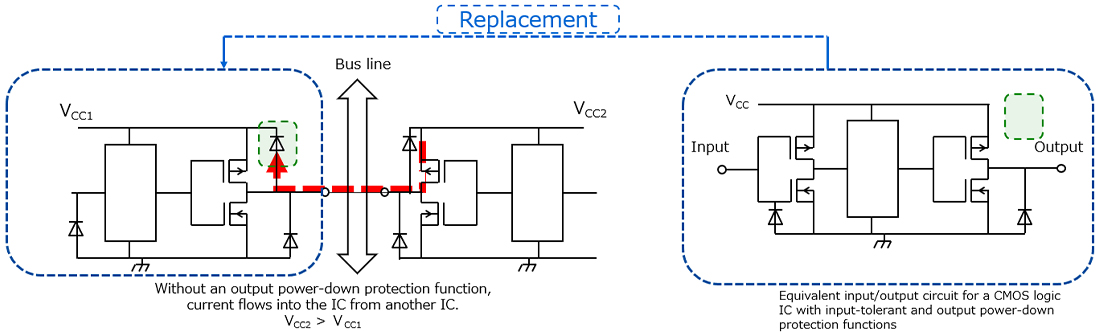
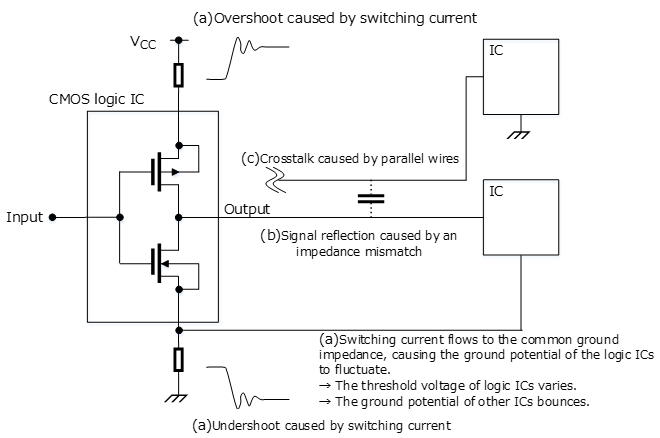
当CMOS IC的输出引脚直接连接到大负载电容时,其传输延迟将增加。此外,进出电容的充电/放电电流增加可能会导致噪声或接合引线烧坏。由于电流在掉电时流向输出寄生二极管,所以CMOS IC不应直接连接到大负载电容。
如果需要将电容器直接连接到CMOS IC的输出端以增加其延迟时间或过滤噪声,则其电容应为500pF或更小。当需要较大的电容时,应在如下所示的IC输出端和电容器之间连接限流电阻(R)。具有输出容限功能的CMOS IC不需要限流电阻(R)来断电。但可能需要一个限流电阻(R)来限制进入电容的充电电流。
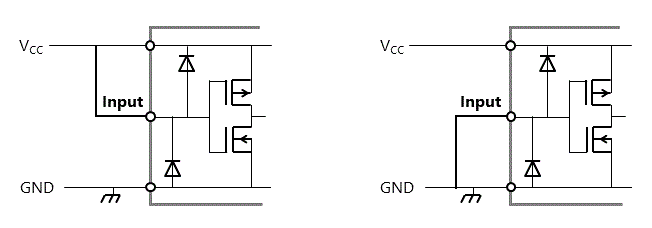
当电容由于掉电而放电时,电流流向内部保护二极管,该二极管通过输入引脚返回到VCC。
如果是输入引脚,当电容由于掉电而放电时,电流流向内部保护二极管,并返回至VCC。
因此,大负载电容也不应直接连接到输入引脚。最高500pF的电容器可直接连接到CMOS IC的输入端,但如果需要更大的电容器,则应在如下所示的IC输入端和电容器之间连接限流电阻(Rs)。