- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
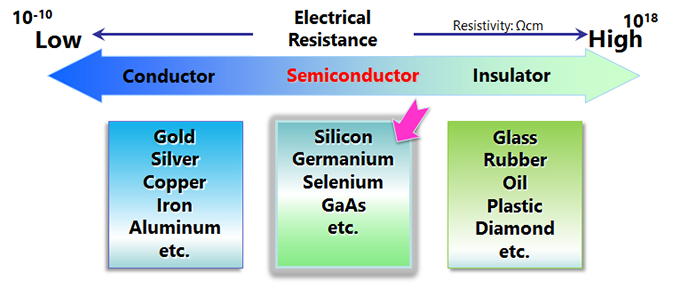
什么是化合物半导体?
下载“第Ⅰ章:半导体基础” (PDF:1.2MB)
Compound semiconductors are compounds made of two or more elements, unlike semiconductors made of a single element such as Si, which is the mainstream of semiconductors.
There are compound semiconductors that combine elements from group III and group V, elements from group II and group VI, and elements from group IV. Examples include GaAs, InP, InGaAlP, and SiGe, which have traditionally been used as high-frequency devices and optical semiconductors. InGaN has also attracted attention as a blue LED and laser diode, and SiC and GaN have been commercialized as materials for power semiconductors.
Compound semiconductors used in devices have higher mobility (high frequency, high switching, high efficiency) than single-element semiconductors such as Si, and have a wide band gap (high temperature operation, high voltage resistance) due to the strong bonding force between atoms. As a result, compound devices are used in power devices, optical devices such as LEDs, and high-frequency devices. Semiconductors with wide band gaps, including single-element semiconductors (such as diamond), are also called wide-band gap semiconductors.
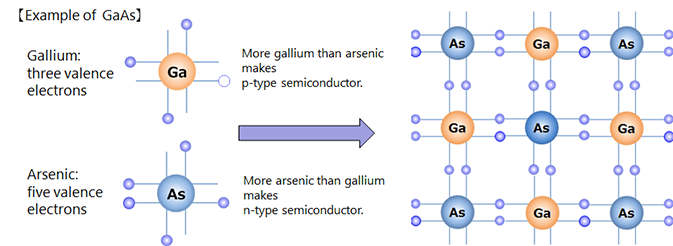
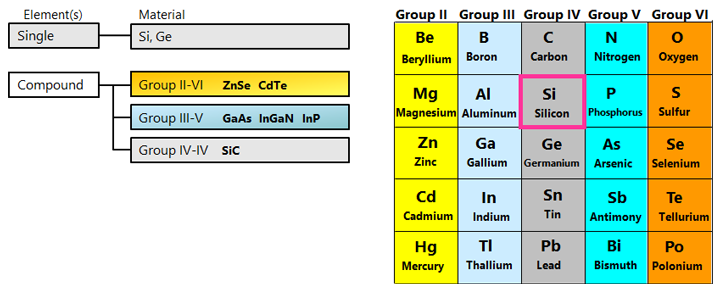
典型的化合物半导体
第Ⅱ-Ⅵ组:ZnSe
第Ⅲ-Ⅴ组:GaAs,GaN,InP,InGaAlP,InGaN
第Ⅳ-Ⅳ组:SiC,SiGe