- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
什么是反向导通IGBT(RC-IGBT)?
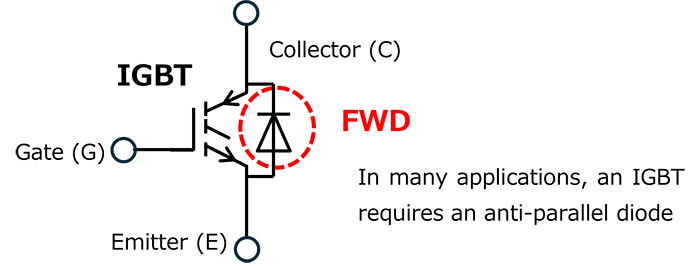
Back electromotive force is generated when controlling the on/off of an inductive load (such as a motor or coil) in an inverter or converter circuit. When using an IGBT for this on/off control, a freewheeling diode (FWD*1) connected in inverse parallel to the IGBT as shown in Fig. 1 is required to process the back electromotive force. A reverse conducting IGBT (RC-IGBT) is a product that combines an IGBT and FWD on a single chip.
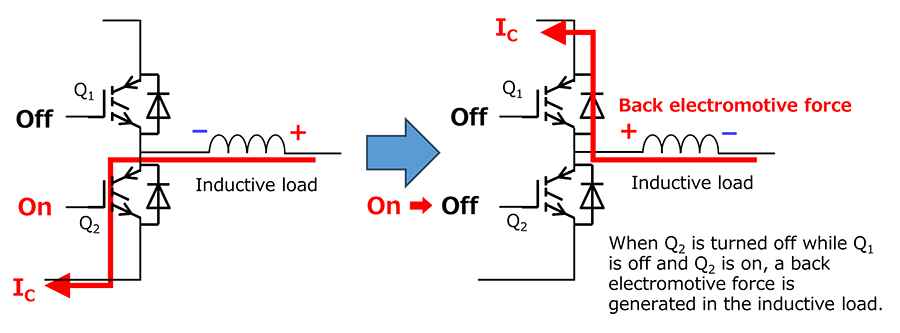
An inductor, which is an inductive load, has the characteristic of generating a back electromotive force (reverse voltage) in response to changes in the load current, preventing changes in the current. In inverter and converter circuits, switching operations that turn inductive loads on and off are repeated. Normally, the on/off transition occurs very quickly, so the back electromotive force is very large. During the transition from on to off, a voltage exceeding the power supply voltage is applied to the IGBT, which may destroy the IGBT.
The load current generated by this back electromotive force is commutated in the reverse direction of the IGBT (from emitter to collector) through the FWD (freewheeling diode) connected in reverse parallel to the IGBT. Fig. 2 shows a circuit in which IGBTs with parallel-connected FWDs are arranged in series as one arm of an H-bridge circuit. When Q2 is turned off, the collector current IC that flows when Q2 is on generates a voltage that exceeds the collector voltage of Q1 due to the back electromotive force generated by the inductive load, causing the FWD to conduct and the current to be commutated.
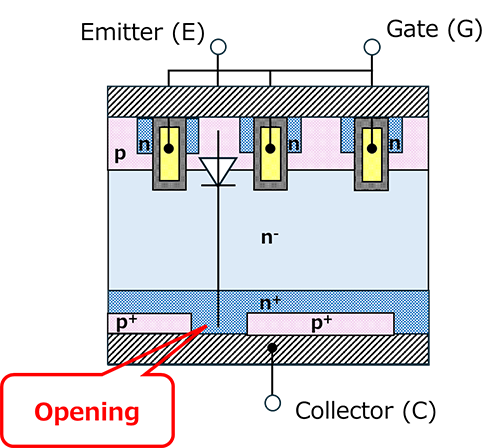
RC-IGBT is a single chip that incorporates this FWD. Fig. 3 shows the internal structure of RC-IGBT. The FWD has an opening in the p+ layer, which is the collector of the IGBT chip, connecting the n+ and collector terminals. This forms a PIN diode (n⁺–n⁻–p⁺ structure) between the emitter and collector electrodes, connected in anti-parallel with the IGBT. RC-IGBTs are used in soft switching applications such as ZVS (Zero Voltage Switching), and more recently have begun to be used in hard switching applications such as inverter circuits. However, due to trade-offs (such as the on-voltage of the IGBT and the reverse recovery time of the FWD), it is difficult to optimize both performances, so compatibility must be confirmed for applications that place importance on high-speed performance or forward characteristics.
Please refer to the following FAQ for information on IGBT on-voltage.
Please refer to the following FAQ for information on soft switching such as ZVS.
Please refer to the following FAQ for information on FWD reverse recovery time.
*1: FWD: An abbreviation for Free Wheeling Diode. It is used as a path (commutation path) for the back electromotive force generated in the reactance load.
*2: PIN diode: A diode that has a high-resistance I layer (intrinsic layer: close to an intrinsic semiconductor, with a low impurity concentration and high resistance) sandwiched between a P layer and an N layer. This structure is used for the FWD of IGBTs, which require high withstand voltages.
相关信息
The following documents also contain related information.
参数搜索
IGBT/IEGT
常见问题(FAQ)
* Company names, product names, and service names used in this FAQ may be of their respective companies.



