- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
为何在运算放大器中使用反馈?
典型运算放大器的开环增益约为105(100 dB)。如果没有反馈,运算放大器由于增益灵敏度高而使电路设计变得困难。负反馈可以将增益和截止频率设置为所需值,从而提高其稳定性并减少性能变化、部件之间的变化以及对温度和其他环境参数的敏感性。
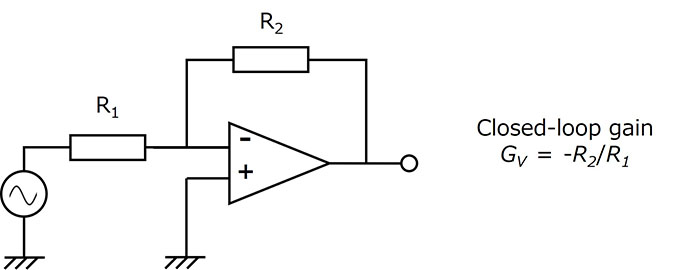
图1显示了反相放大器。此负反馈电路的闭环增益(Gv)可简单地用下式表示:
Gv=-R2/R1
此公式表明闭环增益仅由外部电阻比决定,而不受环境因素的影响。
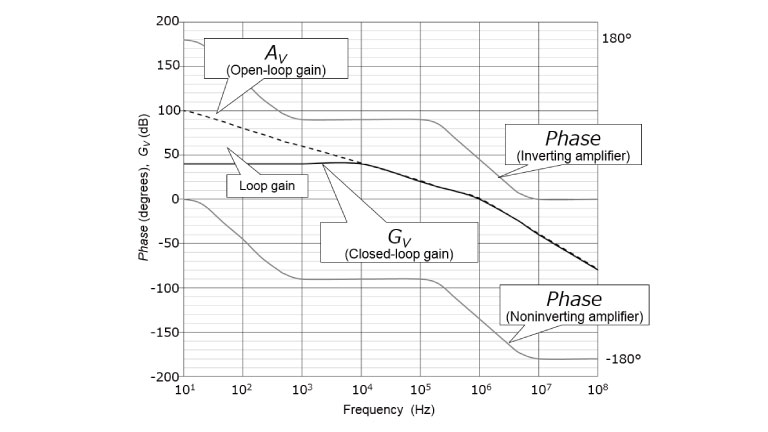
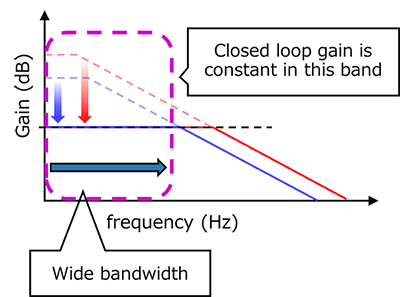
图2显示了典型运算放大器的波特图。开环增益(即无负反馈的增益)按6dB/oct(=20dB/dec)的速率减小。相反,闭环增益在此图中具有从DC至10kHz的恒定增益(取决于运算放大器的频率响应)。如本例所示,可使用反馈为放大器提供带宽。
此外,虽然普通运算放大器(无负反馈)直流区域的开环增益具有非常高的增益,但也存在变化。 通过应用负反馈,增益被固定为由外部电阻设置的增益(闭环增益),从而可以吸收开环增益的变化。

相关链接
以下文档也包含相关信息:
FAQ
应用说明
*本文提及的公司名称,产品名称和服务名称可能是其各自公司的商标。