- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
使用运算放大器可配置成哪些类型的放大器电路?
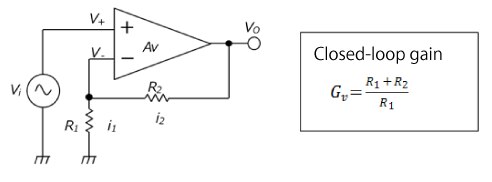
通常,在最基本的电路中,运算放大器均用作电压放大器,具体可分为同相放大器和反相放大器。此外,运算放大器还常用作电压跟随器(亦称为“缓冲放大器”,或简称为“缓冲器”)。运算放大器还可配置成许多其它电路,包括差分放大器和积分电路。图1是一个同相放大器示例。R1和R2均为外部电阻。在此电路中,负反馈用于通过R1和R2将一部分输出电压施加至反相输入端。此电路的闭环增益*1(GV)仅用R1和R2表示。便于设置增益是运算放大器的优点之一。
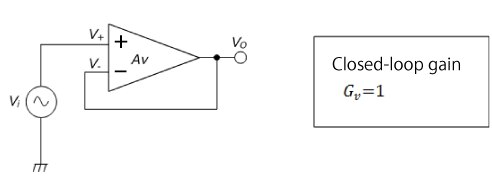
图2显示了一个电压跟随器。在此电压跟随器中,R1为无穷大,R2为零。因此,所有输出电压均施加至反相输入端。由于V+与V-处于虚拟短路*2状态,故输出电压等于输入电压。
电压跟随器通常用作缓冲器,由于输出阻抗低,其可用于阻抗变换。
图3显示了反相放大器。R1和R2均为外部电阻。与同相放大器一样,反相放大器也使用负反馈。因此,可使用图3所示的简单公式计算反相放大器的闭环增益。
*1 请参阅常见问题(FAQ)“什么是运算放大器的开环增益和闭环增益?”
什么是运算放大器的开环增益和闭环增益?
*2 请参阅常见问题(FAQ)“什么是运算放大器虚拟短路?”
什么是运算放大器虚拟短路?

相关链接
以下文档也包含相关信息: