- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
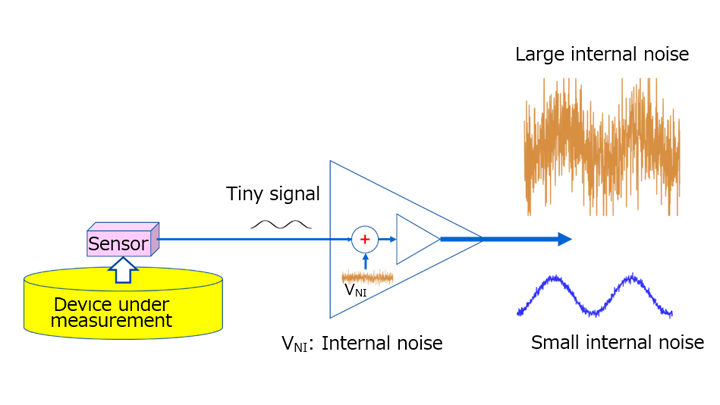
3-3运算放大器的内部噪声
运算放大器用于放大来自传感器或其它器件的微小信号。噪声加至这个微小信号中,并被运算放大器放大。因此,噪声会降低传感器的灵敏度和精度。
与运算放大器相关的噪声分为由电磁干扰和外部器件导致的外部噪声以及内部噪声。本节重点介绍运算放大器的内部噪声。
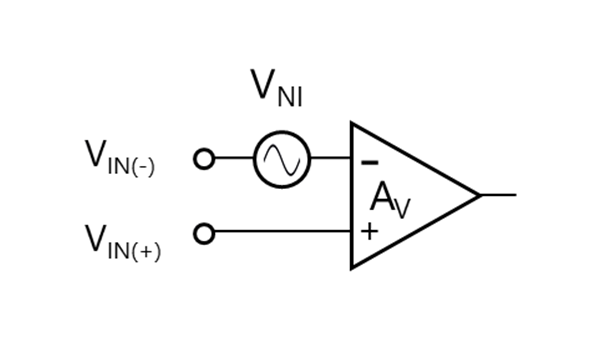
将两种内部噪声定义为等效输入噪声:
- 取决于频率的1/f噪声:电阻器产生的热噪声以及半导体中自由移动的载流子产生的散粒噪声
- 与频率无关的白噪声:由晶体缺陷导致的闪烁噪声以及突发噪声
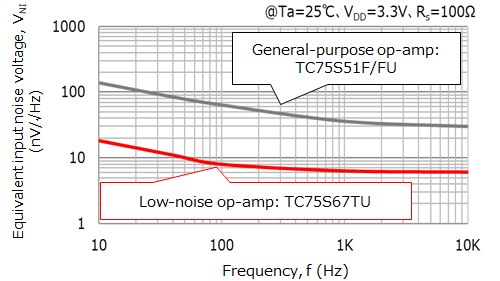
图3-9显示了运算放大器的噪声频率特性,图3-10显示了一个实测等效输入噪声电压示例。图3-10比较了东芝的TC75S51通用运算放大器和TC75S67低噪声运算放大器。
通用运算放大器的白噪声约为30nV/√Hz,转角频率为300Hz,而低噪声运算放大器的白噪声约为6nV/√Hz,转角频率为100Hz。
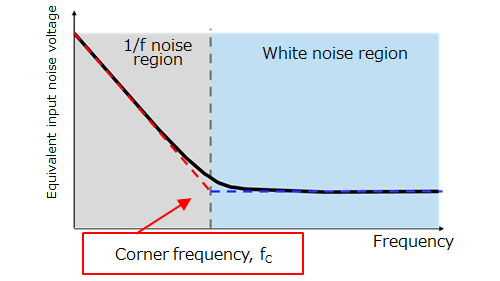
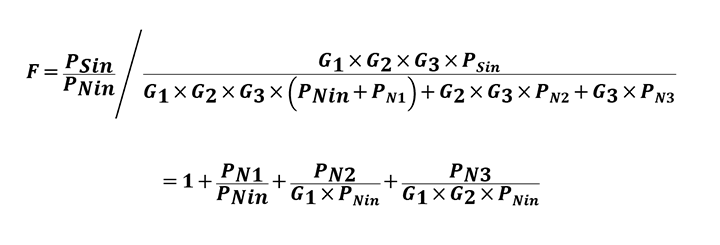
1/f噪声和白噪声均出现在运算放大器的输入端,并且都被定义为等效输入噪声电压。等效输入噪声被增益放大并出现在输出端。需特别注意低频噪声,因为它的电压取决于频率。
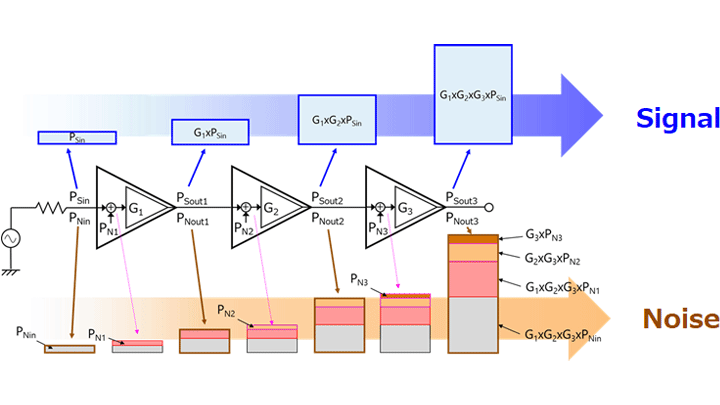
为放大微小信号,有时会级联多个放大器以防止异常振荡。我们来看下每个放大器级如何影响出现在级联放大器输出端的噪声。
图3-11显示了一个三级级联放大器。
如图3-11所示,可按下式计算输出信号功率(PSout3)和输出噪声功率(PNout3)。
如您所见,第一级放大器的输入噪声(PNin)和等效输入噪声(PN1)对输出噪声的影响最大。
用以下等式表示输出信号功率(PSout3)和输出噪声功率(PNout3):
PSout3=G1×G2×G3×PSin
PNout3=G1×G2×G3×(PNin+PN1)+G2×G3×PN2+G3×PN3
因此,可按下式计算噪声系数(F,这是一个噪声的度量):
第二级放大器的等效输入噪声(PN2)除以第一级增益(G1),而第三级放大器的等效输入噪声(PN3)除以第一级增益和第二级增益(G1和G2)。因此,各放大器连续级的输入噪声对输出PNout3的影响逐渐降低。如本例所示,应在第一级使用低噪声放大器以减少其噪声的影响。