- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
1-3. pn结
在讨论肖特基势垒二极管(SBD)之前,我们先了解一下pn结的工作原理,因为它是构成二极管的最基本结。
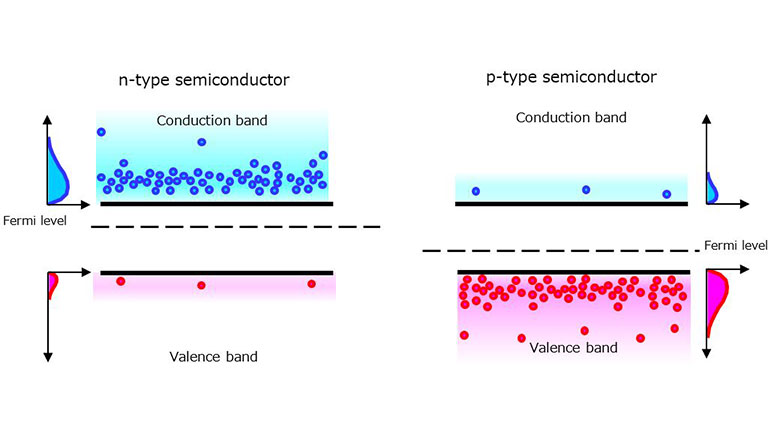
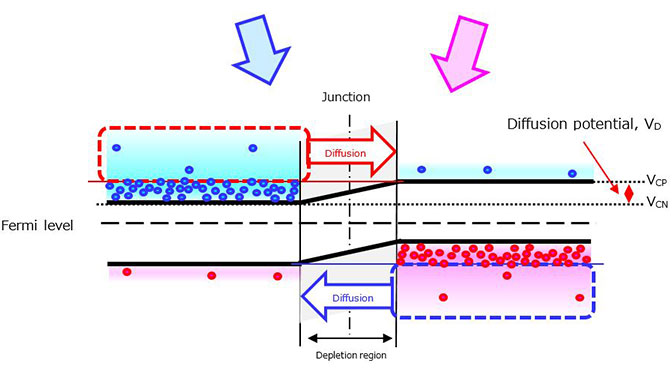
当p型半导体和n型半导体相连时,它们的费米能级会相等。这会在n型半导体和p型半导体(分别为VCN和VCP)的导带的下边缘之间产生一个电位差。这种电位差称为扩散电位(VD)或内建电位。
电子是n型半导体中的主要电荷载流子,而空穴是p型半导体中的主要电荷载流子。在结附近,n型半导体中的电子和p型半导体中的空穴被吸引并相互结合然后消失,从而形成一个称为耗尽层的区域,该区域中不存在载流子。然后,n型半导体中的一些电子扩散至p型半导体中,因为它们的能量超过了VD。因此,当在VD以上时,两个半导体中的电子密度会相等。同样,p型半导体中的一些空穴扩散至n型半导体中。由于电荷载流子(电子和空穴)扩散而流动的电流称为扩散电流。在结上施加电压(即电场)也会导致漂移电流流动。然而,除耗尽区外,扩散电流占主导地位。当pn结无偏置时,一旦结达到平衡状态,电流就会停止流动。