- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
40V/2A步进电机驱动IC采用先进的微步驱动技术,助力实现电机高效、低振动、低噪声运行
东芝电子元件及存储装置株式会社(简称“东芝”)现已推出新一代步进电机驱动IC“TB67S579FTG”。该产品采用先进的微步驱动技术,为消费和工业应用提供高效、低振动和低噪声的电机运行。TB67S579FTG是一款2相双极型步进电机驱动IC,采用恒流控制法,支持电机输出电压额定40V和电机输出电流额定2.0A[1]。
近年来,电池供电的电机驱动设备如标签打印机需要高效率以降低功耗。使用电机进行位置控制的设备,如3D打印机和监控摄像头,也需要减少振动和噪声。为满足这些市场需求,新产品集成先进的微步驱动技术,包含三大关键功能:“第二代主动增益控制(AGC2)”、“自动波形生成系统(AWGS)”、“连续微步进”。
AGC2是一个根据负载调整电机驱动电流来控制步进电机的功能。通常,步进电机在峰值负载条件下以最大电流持续驱动。然而,通过使用此功能,电机可以在低负载条件下以最低必要驱动电流运行。因此,这使电机运行效率高,并降低设备的功耗。
AWGS是一种功能,它能够利用原本用于全步旋转控制的CLK信号[2],以微步模式驱动步进电机。采用此功能后,即使在典型应用场景下(例如,最初以全步模式驱动步进电机以快速产生转矩,再切换为微步驱动模式以降低振动和噪声),亦可实现平滑过渡,无需调整控制信号。此功能可以显著降低微控制器单元(MCU)等控制器件上的处理负载。
与现有的微步驱动方法相比,连续微步驱动可使电机驱动电流更接近正弦波,有助于实现步进电机的低振动、低噪声运行。
新产品采用小型封装VQFN48。此外,通过消除电机输出电流检测所需的外部电阻以及内置电荷泵电容器,能够减少外部元件数量,从而节省安装板上的空间。
东芝将继续开发适合各种应用的产品,力求简化用户设计、减小电路板空间以及提供综合解决方案。
注:
[1]实际电机驱动电流会根据工作环境变化,包括环境温度和电源电压等因素。
[2]CLK信号是一种用于控制步进电机驱动器中电机阶跃运动的定时信号。电机的转速会根据CLK信号的频率变化。
特点
- 第二代主动增益控制(AGC2)提升电机驱动效率。
- 自动波形生成系统(AWGS)降低MCU及其他控制IC的处理负担。
- 连续微步进实现低振动和低噪声运行。
特点说明
1.第二代主动增益控制(AGC2)提升电机驱动效率
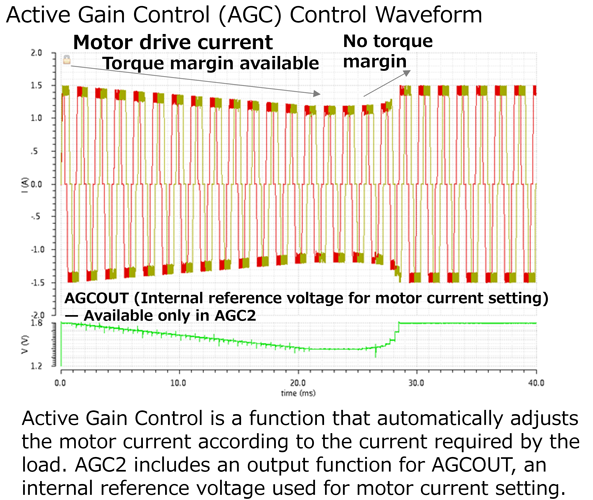
主动增益控制(AGC)是一种在电机运行过程中检测感应电压以确定负载,并根据外部负载自动调整电机驱动电流的功能。当负载较重时,电机驱动电流增加;当负载较轻时,负载会降低。该机制使电机能够以最小所需电流运行,使得比传统方法更高效的电机驱动。
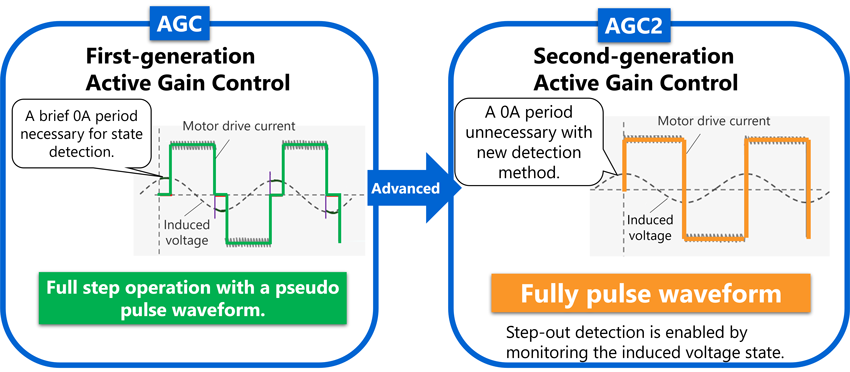
第一代AGC在OFF周期(输出电流为0%)检测感应电压,即使在全步运作中也需要短暂的0%间隔。因此,转速相对于预期的电流波形受到限制。第二代AGC2实现了高速旋转[3]同时通过预测0%间隔的时序并相应检测感应电压,保持预期的全步波形。它还配备了一个端子,可以以电压信号的形式监测实际的电机驱动电流。
2. 自动波形生成系统(AWGS)降低MCU及其他控制IC的处理负担
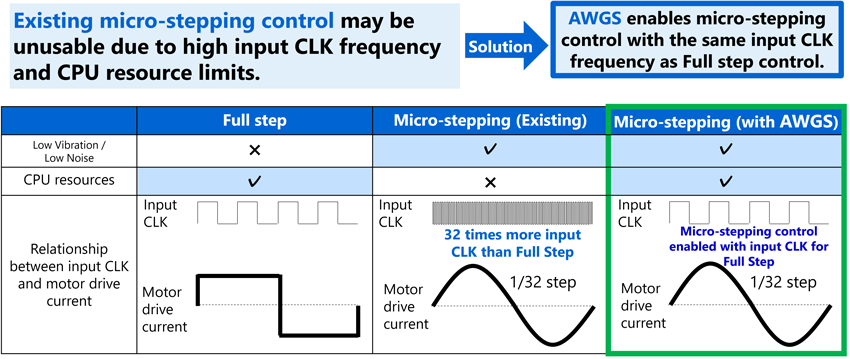
自动波形生成系统(AWGS)是一个功能,使得在与全步控制相同的CLK频率下实现微步进控制。此前,输入CLK频率需与CLK步数成比例增加。通过AWGS,可以在不改变CLK频率的情况下使用微步进控制,从而简化了MCU的控制。
3.连续微步进实现低振动和低噪声运行
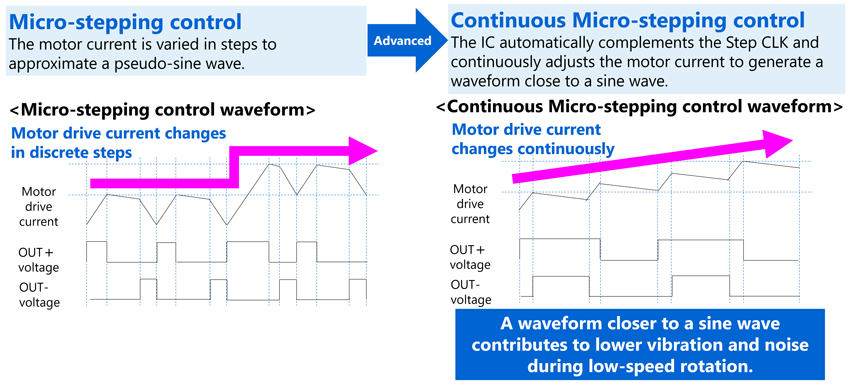
连续微步进通过允许IC自动补偿步进CLK并持续调整电机驱动电流,实现更接近正弦波的驱动波形。这有助于进一步减少低速旋转时的振动和噪音[4]。
注:
[3]主动增益控制(AGC)的转速根据所使用的具体电机和外部负载的情况而变化。
[4]振动和噪音的程度可能因电机和实际驱动条件而异。
应用
- 多功能打印机(MFP)
- 喷墨打印机
- 标签打印机
- 3D打印机
- 监控摄像头
- 投影仪
- 缝纫机
主要规格
(除非另有规定,Ta=-40至85°C)
| 器件型号 | TB67S579FTG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 支持的电机 | 2相双极型步进电机 | ||||
| 绝对最大额定值 | 电机输出电压 VOUT(V) |
Ta=25°C | 40 | ||
| 电机输出电流 IOUT(A) |
Ta=25°C | 2.0 | |||
| 工作范围 | 电机电源VM(V) | 4.5至34 | |||
| 工作温度Topr(°C) | -40至85 | ||||
| 电气特性 | 输出晶体管漏极与源极之间的导通电阻(纵向总和) RON(D-S)(Ω) |
IOUT=2.0A,Tj=25°C | 典型值 | 0.6 | |
| 电流消耗IM1(μA) | 输出:开路,休眠模式 | 最大值 | 1 | ||
| 接口 | 时钟(CLK)输入控制 | ||||
| 电流检测方法 | 无外接电阻 | ||||
| 电荷泵的电容器 | 不需要 | ||||
| 步进模式 | 全步到1/32步模式 | ||||
| 先进的微步驱动技术 | 第二代主动增益控制(AGC2)、自动波形生成系统(AWGS)、连续微步进 | ||||
| 异常检测功能 | 过电流检测、过温检测、供电电压欠压检测、失速检测和开路负载检测 | ||||
| 封装 | 名称 | P-VQFN48-0707-0.50-006 | |||
| 尺寸(mm) | 典型值 | 7.0×7.0 | |||
| 库存查询与购买 |  |
||||
购买、样品、及IC可靠性查询
库存查询与购买
请输入3个以上字符
Through this website you are able to proceed to the website of our distributors ("Third Party Website") which is not under the control of Toshiba Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "Toshiba"). The Third Party Website is made available to you as a convenience only and you agree to use the Third Party Website at your own risk. The link of the Third Party Website does not necessarily imply a recommendation or an endorsement by Toshiba of the Third Party Website. Please be aware that Toshiba is not responsible for any transaction done through the Third Party Website, and such transactions shall be subject to terms and conditions which may be provided in the Third Party Website.
*本文提及的公司名称、产品名称和服务名称可能是其各自公司的商标。
*本文件中所含信息,包括产品价格和产品规格、服务内容及联系方式,仅于公告当日有效,如有更改,恕不另行通知。

