- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
车载3相无刷电机栅极驱动电路IC:TB9084FTG
具有车载应用所需的最基本功能和多功能特点的栅极驱动电路IC。适用于使用3相无刷电机的车身系统、泵和电动发电机。
<本产品特点>
车载设备中使用的电机数量继续增加,3相无刷电机在长使用寿命和静音性能方面相对更优,其发展令人瞩目。东芝电子元件及存储装置株式会社(简称“东芝”)目前正在努力加强其产品线以满足该需求,这里介绍的TB9084FTG就是增强产品之一(表1)。
表1:适用于3相无刷电机的东芝车载栅极驱动电路IC产品线
| 器件型号 | 状态 | 封装 | GD | CP | MC SA |
SR的GD | SPI | 注释 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB9081FG | MP | LQFP64 | ○ (3相) |
○ (3 TBV) |
○ (三通道) |
○ (五通道) |
○ |
EPS的全部功能。ASIL-D支持。 |
| TB9083FTG | MP | QFN48 | ○ (3相) |
○ (3 TBV) |
○ (三通道) |
○ (三通道) |
○ |
TB9081的精简版本。(例如,安全继电器的驱动通道数量)ASIL-D支持。 |
| TB9084FTG | MP | QFN36 | ○ (3相) |
○ (3 TBV) |
○ (单通道) |
○ (单通道) |
○ |
针对各种应用的TB9083精简版本。(例如,删除了安全继电器栅极驱动电路和诊断功能、减小了驱动电流能力) |
| TPD7212F | MP | QFN32 | ○ (3相) |
○ (3 TBV) |
- | - | - | 具有最基本功能的多用途器件。 |
过去,“TPD7212F”(最基本的必要功能)和“TB9083FTG”(ASIL-D[2]功能)在功能方面存在很大的差距,而TB9084FTG将消除这种差距并满足各种客户需求。
车载设备所需的最基本功能
TB9084FTG驱动外部N沟道MOSFET,外部N沟道MOSFET驱动3相无刷电机。由于电压输出至该栅极,因此称为栅极驱动电路IC。它还有一个输出引脚通道来控制外部N沟道MOSFET。它可用于防止电池反接,适用于电源关断继电器等器件。关于SPI通信,除了具有读取异常检测标志的功能外,它还具有设置正常和异常状态之间的阈值以及配置检测到异常状态后的反应操作等功能,使其能够适应各种应用。此外,它还有一个运算放大器通道,专门监控电机电流。该运算放大器具有校准输入补偿电压的功能,执行此功能后,标准条件下[3]的输入补偿电压为±1 mV。
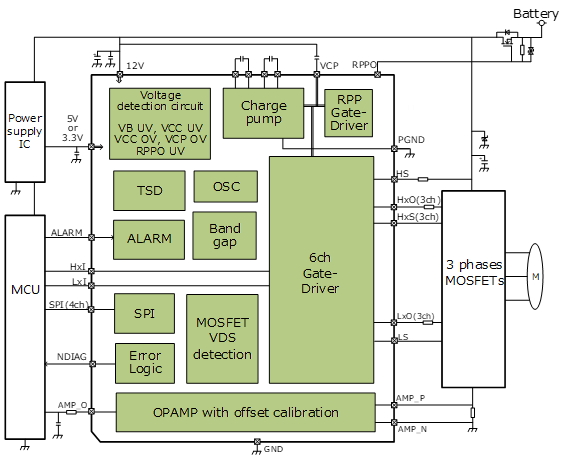
UV表示欠压,OV表示过压,TSD表示过热保护,OSC表示振荡器,RPP表示极性反接保护,SPI表示串行外设接口,OPAMP表示运算放大器,MCU是单片机的缩写。除了驱动3相无刷电机外,它还具有车载应用所需的最基本功能,可检测系统异常,具有配套的保护功能。
TB9084FTG产品价值1:
有助于确保系统设计的灵活性
TB9084FTG可贴装在由微控制器、N沟道MOSFET、电源IC和通信PHY[4]等单独元器件组成的ECU中(图2右侧)。虽然这种结构在元器件总尺寸和成本方面存在缺点,但它足够灵活,可以适应系统要求的变化;当发生变化时,只需更换相关元器件即可。另一方面,有一种结构是通过硬逻辑执行电机控制(图2左侧)。这种结构在总尺寸和成本方面具有优势,但它对电机周围环境变化的响应能力有限。另一种结构是由微控制器执行电机控制,而其外围元器件集成到单个产品中(图2中间)。这种结构能以最合理的方式平衡优缺点。但是,通常被视为通用元器件的微控制器的处理能力很有限,当系统要求的变化超出其处理能力时,微控制器以外的功能也会更新,因此变化往往会很大。
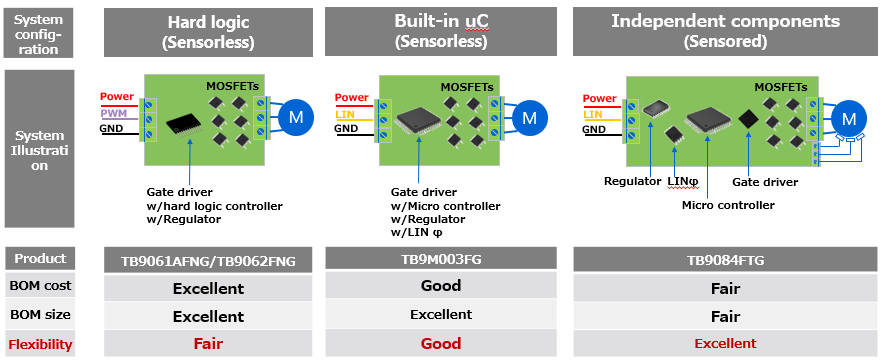
东芝能够提供上述所有三种结构的产品,并提供最佳解决方案以满足各种系统要求。
有关图2中所列产品的更多信息,请参阅以下页面。
TB9084FTG产品价值2:
有助于减小ECU的尺寸
通过最小化功能设计,可采用小型封装方案,6×6mm VQFN36封装,从而有助于实现设备的小型化。该封装还采用可润湿侧翼[5]结构,便于通过目视检查确认焊点可靠性。
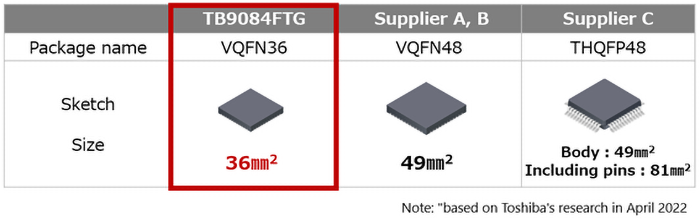
本产品的QFN封装方式为可焊锡封装,考虑到车载应用,这种封装方式提高了贴装可靠性和可检查性。另外,通过将具有地电位(GND)的边角引脚隐藏在模具树脂中,可降低因引脚间短路故障而导致误动作的风险。
TB9084FTG主要规格
电源(VB、VCC)适用于12 V电池系统和搭电启动环境。质保芯片温度范围为-40°C至175°C,相当于AEC-Q100中的0级[6]。关于栅极驱动电路的电气特性,即使在低VB电源下,其输出电压也足以驱动外部N沟道MOSFET。其电流能力使栅极输入电荷(Qg)约为55 nC且ID[7]相当于50 A的MOSFET能以20 kHz的频率进行PWM[8]控制。主要规格如下所示。.
请参阅以下页面,了解符合这些特性的MOSFET。
推荐的MOSFET(TPH1R104PB)
绝对最大额定值(节选)
| 规格编号 | 项目 | 端子 | 符号 | 绝对最大额定值 | 单位 | 条件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.1 | 电源 | VB | Vb | -0.3至28(DC) | V | 1V/s<Vb<8V/μs (设计值) |
| 8.2 | 28至40(≦1 s) | |||||
| 8.3 | VCP | Vcp | -0.3至60(DC) | - | ||
| 8.4 | VCC | Vcc | -0.3至6 | 1V/s<Vcc<0.3V/μs (设计值) |
工作电压范围(节选)
| 规格编号 | 项目 | 端子 | 符号 | 工作电压范围 | 单位 | 条件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.1.1 | 输入电压 | VB | Vb | 5.7至28 | V | DC |
| 9.1.2 | VCC | Vcc | 3.0至5.5 |
电气特性(节选)
除非另有规定,Vb=5.7至28 V,Vcc=3.0至5.5 V,Tj=-40至175 °C
| 规格编号 | 项目 | 端子 | 符号 | 条件 | 最小值 | 典型值 | 最大值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.3.1 | 电荷泵输出电压 | VCP | Vcph1 | 5.7 V≦Vb<7 V 负载=-10 µA至-13 mA |
Vb+7.5 | Vb+9.3 | Vb+12.5 | V |
| 9.3.2 | Vcph2 | 7 V≦Vb≦28 V 负载=-10 µA至-13 mA |
Vb+9 | Vb+12 | Vb+14.5 | |||
| 9.4.5 | 高边外部MOSFET的栅极驱动电路输出电压 | HUO, HVO, HWO |
Voh1 | Voh1=H*O - H*S 负载=-100 μA 7V≦Vb≦28 V,H*S=0 V |
7 | 10 | 12 | |
| 9.4.6 | Voh1_2 | Voh1_2=H*O - H*S 负载=-100 μA 5.7 V≦Vb<7 V,H*S=0 V |
Vcp-0.3 | - | Vcp | |||
| 9.4.7 | Vol1 | Vol1=H*O - H*S 负载=100 μA |
0 | 0.2 | ||||
| 9.4.8 | 低边外部MOSFET的栅极驱动电路输出电压 | LUO, LVO, LWO |
Voh2 | Voh2=L*O - LS LS=0 V 负载=-100 μA |
6.7 | 11 | 12 | |
| 9.4.9 | Vol2 | Vol2=L*O - LS 负载=100 μA LS=0 V |
0 | - | 0.2 | |||
| 9.4.11 | 栅极驱动电路源输出电阻 | HUO, HVO, HWO, LUO, LVO, LWO |
Rohh | HUI,HVI,HWI=VCC LUI,LVI,LWI=VCC 负载=-50 mA |
- | 8.8 | 24 | Ω |
| 9.4.12 | 栅极驱动电路灌电流输出电阻 | Rohl | HUI,HVI,HWI=0 V LUI,LVI,LWI=0 V 负载=50 mA |
3 | 6 |
高边MOSFET的栅极驱动电路根据VB电压状态切换输出电路接线方式。当VB电压足够时,由于电荷泵电压足够,因此输出钳位电压(规格编号9.4.5)。 当VB电压不足时,电荷泵电压也很低,因此电荷泵电压按原样输出(规格编号9.4.6)。
免费借用产品评估板
为使客户能够轻松验证TB9084FTG的特性,我们免费提供评估板。请联系我们的销售人员或业务伙伴。
评估板的尺寸为150 mm×160 mm。该IC的贴装位置略偏向中心左下方。为方便客户,将根据实际需要安装开关、跳线和连接器。
东芝目前正在努力加强用于控制车载设备电机的IC产品线。我们将向市场推出可优化IC内置功能和性能以满足客户需求的产品,帮助业界提高车载设备的电气化程度和舒适度。
注:
[1]电子控制单元的缩写,这是一种将电子元器件贴装在电路板上的器件。
[2]ASIL:汽车安全完整性等级,D:D级(A至D级中的最高等级)
[3]Ta=25 ℃,增益设置=15,输入共模电压=0 V,输出负载=0.5 mA
[4]负责OSI参考模型中物理层的IC。物理→PHY。
[5]封装引线侧的形状。一种允许对电路板安装进行自动目视检查(AVI)的端子结构。
[6]汽车电子委员会(AEC)定义的车载IC可靠性测试标准和其他标准。
[7]ID表示流入MOSFET的漏极(D)的电流。
[8]PWM表示脉宽调制,这是一种控制向电机施加电源的方法。
相关信息
购买、样品、及IC可靠性查询
库存查询与购买
请输入3个以上字符
Through this website you are able to proceed to the website of our distributors ("Third Party Website") which is not under the control of Toshiba Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "Toshiba"). The Third Party Website is made available to you as a convenience only and you agree to use the Third Party Website at your own risk. The link of the Third Party Website does not necessarily imply a recommendation or an endorsement by Toshiba of the Third Party Website. Please be aware that Toshiba is not responsible for any transaction done through the Third Party Website, and such transactions shall be subject to terms and conditions which may be provided in the Third Party Website.
*SmartMCD™东芝电子元件及存储装置株式会社的商标。
*本文提及的公司名称、产品名称和服务名称可能是其各自公司的商标。

