- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
什么是二极管?
二极管是一种具有一个PN结或一个金属-半导体结的半导体器件。它有两个端子,称为阳极和阴极。
Diode types and characteristics
Diodes are broadly divided into PN junction diodes and metal-semiconductor junction diodes (Schottky barrier diodes) based on their type of junction. pn junction diodes are further divided into rectifier diodes and Zener diodes. (Fig. 1)
The following FAQ explains the types of diodes.
它具有开关的特性,因此可根据施加在阳极与阴极之间的电压的方向,使电流流动或不流动。这种动作称为整流。
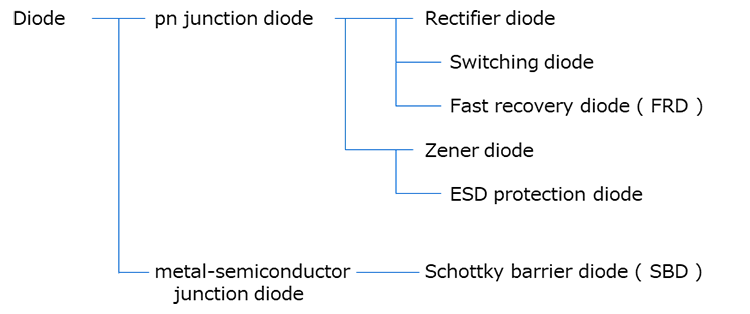
半导体的电导率值介于导电性良好的导体(如金属)和不易导电的绝缘体(如玻璃或橡胶)的电导率之间。例如,硅和锗都是半导体材料。
(有关半导体的更多信息,请参阅e-learning“分立半导体器件基础知识”)
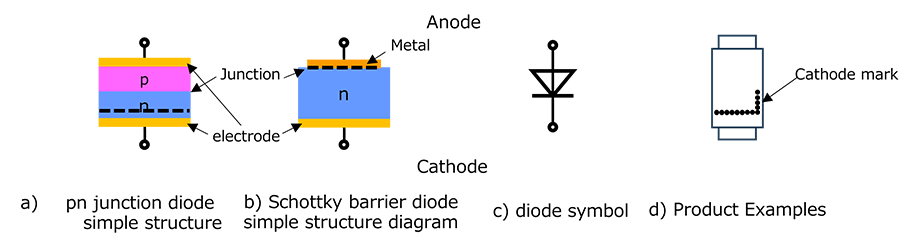
作为二极管材料,使用p型和n型半导体。掺杂有硼(B)或其它电子受体原子的半导体称为p型半导体,因为其中的大部分电荷载流子为正空穴。掺杂有砷或其它电子供体原子的半导体称为n型半导体,因为其中的大部分电荷载流子为负电子。pn结二极管由p型和n型半导体组合而成。例如,通过将以高能量加速的p型(n型)掺杂剂离子注入n型(p型)半导体,生成pn结。
以这种方式形成并附带电极端头的pn结称为二极管。以这种方式形成并附带电极端子的pn结称为二极管。(图1)
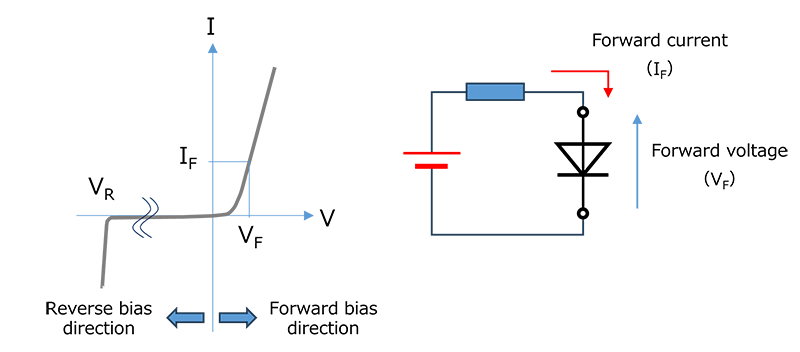
二极管仅在正向偏置时才会传导电流(即当阳极比阴极更加正向偏置时)(图2)。这种只允许电流沿一个方向流动的功能称为整流。
Diode structure and operation
通常二极管在反向偏置时不导通。然而,随着反向偏置电压的增大,大电流会在特定电压下突然通过二极管。此电压称为击穿电压(VBR)。在击穿区域高于VBR时,电压的细微变化会引起电流的大幅变化。换言之,相对于电流变化,电压变化很小。一些二极管专门利用这种恒压特性,例如齐纳二极管和瞬态电压抑制(TVS)二极管(亦称为ESD保护二极管)。
图3显示了pn结二极管的IF-VF曲线。
此外,还有一种二极管使用金属代替p型或n型半导体。由于金属与p型(n型)半导体之间的功函数差异,金属半导体结可以是具有类似于pn结的整流特性的肖特基结,具体取决于金属半导体组合。这种二极管称为肖特基势垒二极管(SBD),其特点是正向电压低。
Diode applications

Diodes are the simplest semiconductor elements and have been used in a wide range of circuits. Some applications have been replaced by ICs, but here are some examples of where diodes are still used today.
- Rectification:
This is the most basic circuit that utilizes the characteristic of diodes that current flows in only one direction. When an AC signal centered on GND is input, the diode turns on at a voltage level that is forward voltage (VF) higher than GND.
Even today, full-wave rectification circuits (diode bridges) that apply this technique are used in many electronic devices.
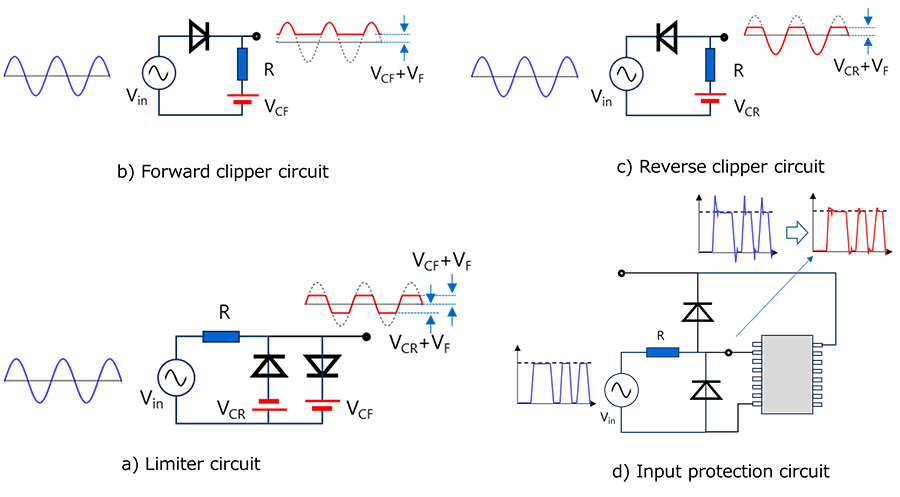
Clipper circuits, limiter circuits:
There are forward clippers and reverse clippers in clipper circuits. One application of this is the limiter circuit. This is still used today for input protection (overvoltage protection) of ICs.
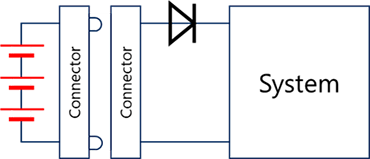
- Reverse battery protection / Reverse current protection:
In cases where there is a possibility of accidentally connecting the polarity in reverse, such as with batteries, a diode is connected in series to the power line. Since normal pn junction diodes have a large insertion loss, Schottky barrier diodes with a small VF are used. However, care must be taken regarding leakage current during reverse bias.
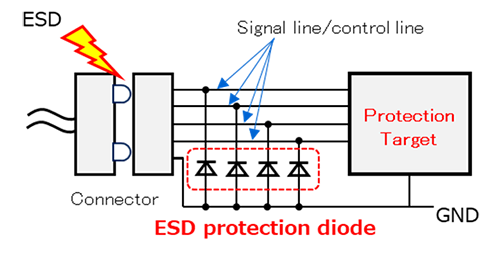
- ESD protection:
Used by connecting between the signal line and GND of an externally exposed terminal (such as a USB terminal) into which ESD may penetrate. An ESD protection diode or Zener diode specially designed for this purpose is used.
Diode packages
Diode packages are mainly two-pin packages with two terminals, an anode and a cathode. We offer mainly surface mount packages ranging from ultra-small to large. There are also multi-pin packages with multiple built-in diodes.
Some examples are shown below.
For details on package dimensions, etc., please refer to the following page.
Diode Package
相关链接
关于产品请参考以下链接。
* Company names, product names, and service names used in this FAQ may be of their respective companies.