- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
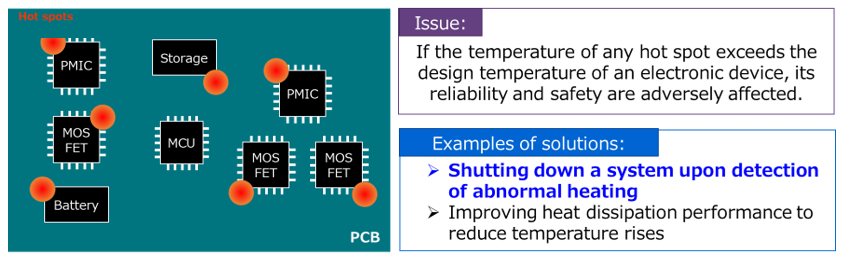
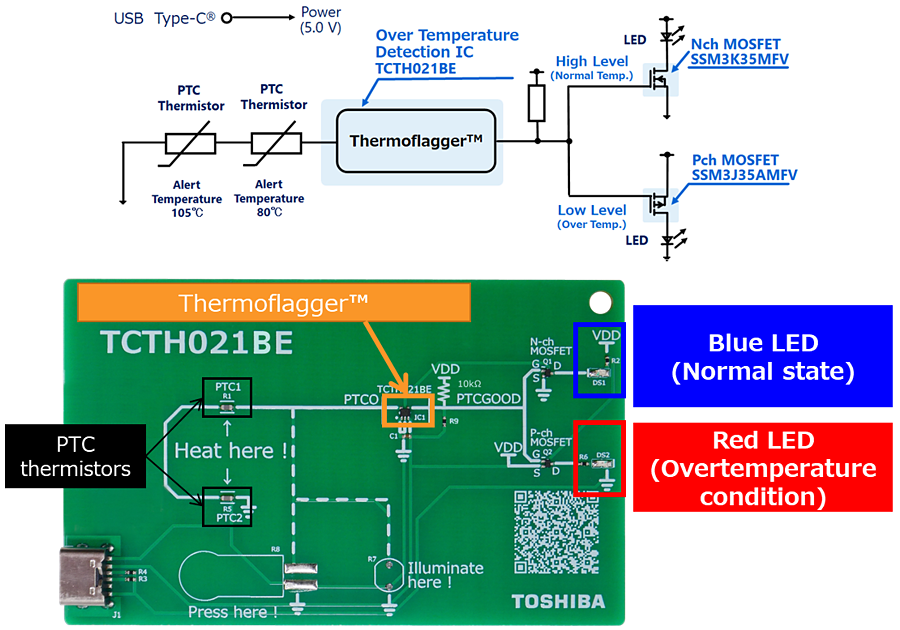
Thermoflagger™的基本操作
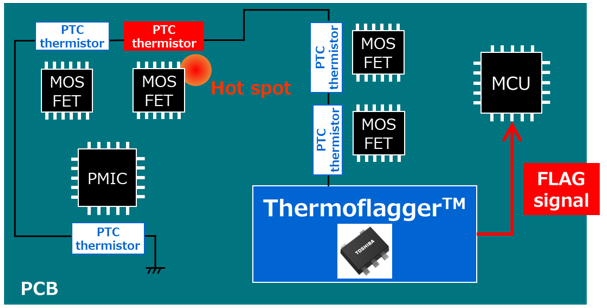
Thermoflagger™ supplies a small constant current to PTC thermistors to detect changes in their resistance (temperature).
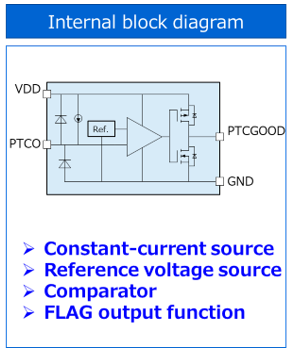
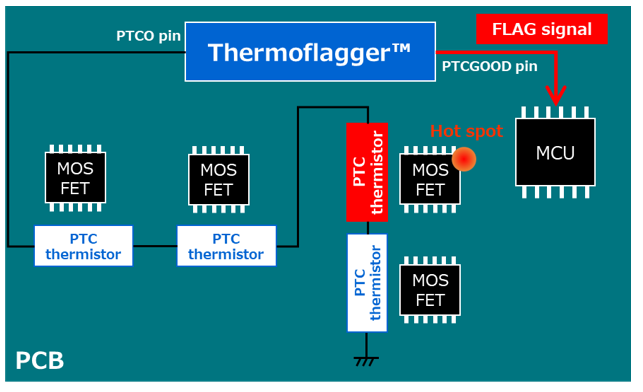
The left-hand figure shows the internal block diagram of Thermoflagger™. It consists of a constant-current source, a reference voltage source, a comparator, and a FLAG output function.
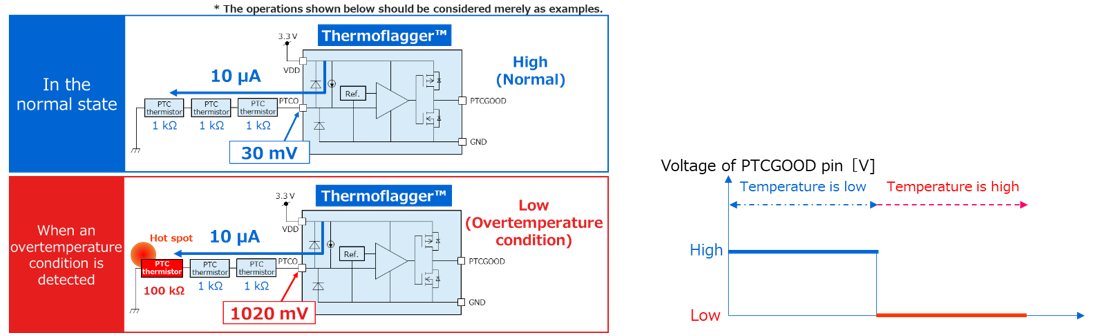
Next, we will briefly explain how it works.
When temperature is low, PTC thermistors have relatively small resistance. Therefore, the voltage at the PTCO pin is low. At this time, the PTCGOOD pin is driven High.
When the temperature of a PTC thermistor increases and reaches the critical temperature, its resistance increases dramatically, causing the voltage at the PTCO pin to increase. At this time, the PTCGOOD pin is driven Low.
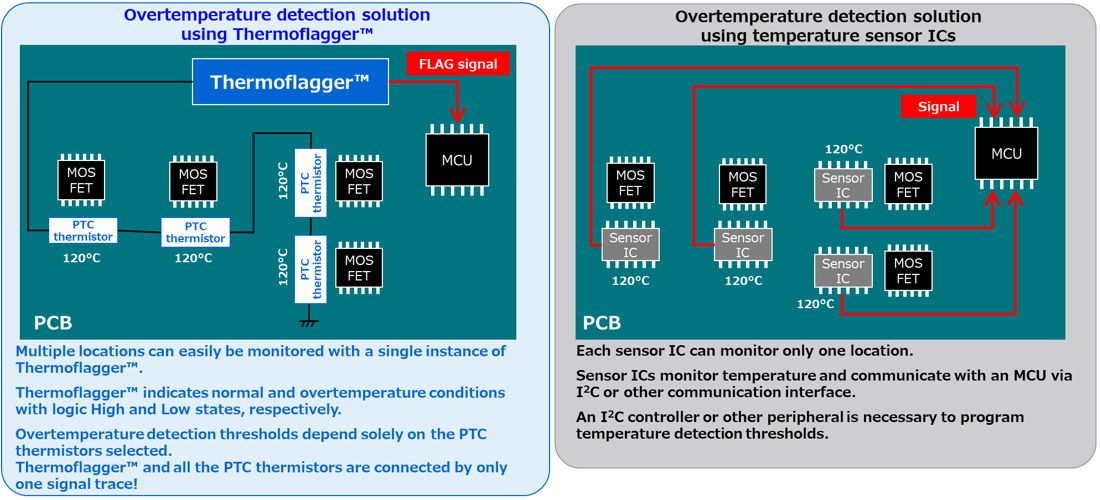
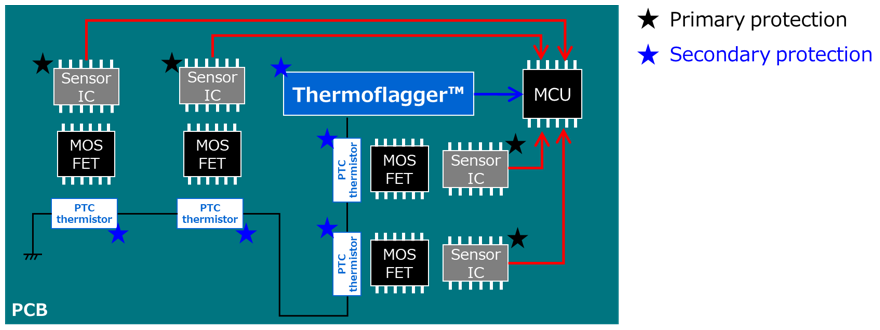
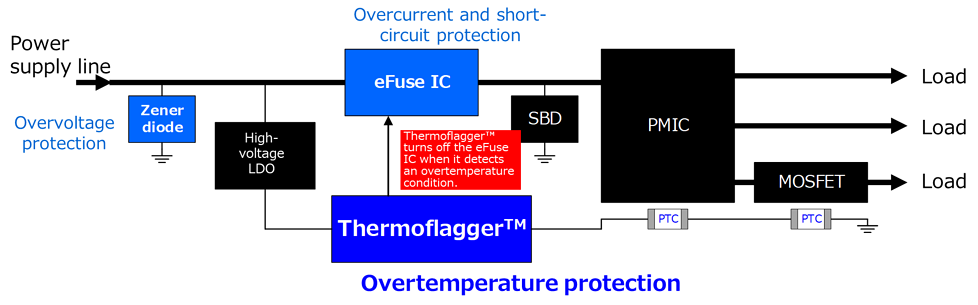
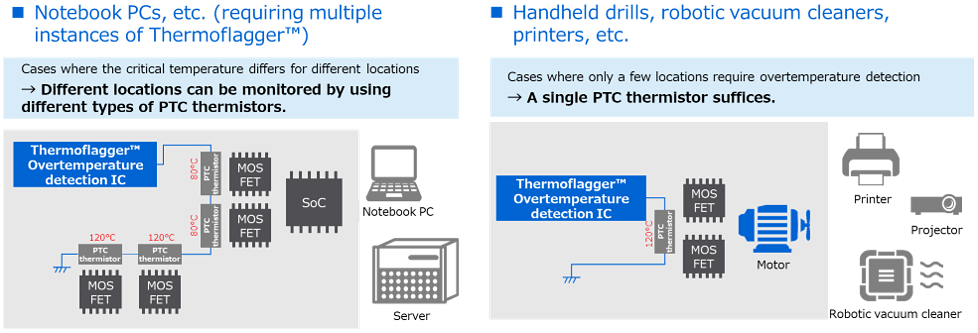
As shown in this figure, you can easily create an overtemperature detection circuit by combining Thermoflagger™ and PTC thermistors.
Basic of Thermoflagger™
Related information
- Product Web Page
- Applidcation Notes
- Catalog
- Parametric searches for all Toshiba Thermoflagger™ products are available here
- Stock Check & Purchase Toshiba Thermoflagger™ here
* Thermoflagger™ is a trademark of Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation.
* Other company names, product names, and service names may be trademarks of their respective companies.