- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
浪涌保护齐纳二极管产品线扩充,新增20款适用于车载设备的小型SOD-523封装产品

东芝电子元件及存储装置株式会社(“东芝”)推出了XCEZ系列适用于车载设备的浪涌保护齐纳二极管,扩大了其产品线。该系列二极管采用小型通用SOD-523封装,适用于高级驾驶辅助系统(ADAS)和电池管理系统(BMS)等车载系统。
近年来,随着车载设备电气化程度的日益提高,对于防止由纳秒级静电放电(ESD)和微秒至毫秒级开关浪涌等噪声引起的故障的需求与日俱增。XCEZ系列产品可抑制穿透了各种车载ECU[1]的电源线路和连接器的噪声引起的系统故障。新产品通过吸收外部噪声和浪涌,为器件和电路提供有效保护。
XCEZ系列采用行业标准的通用SOD-523封装(1.6×0.8mm),相较于东芝现有的SOD-323封装(2.5×1.25mm),可将安装面积减少约59%,从而实现了更高密度的安装。
XCEZ系列与XCUZ系列相似,也采用东芝专有的齐纳工艺以降低动态电阻。该系列中的XCEZ5V6产品,其动态电阻低至0.16Ω(典型值),可有效吸收浪涌电压,从而保护器件与电路,防止系统发生损坏和故障。
XCEZ系列与XCUZ系列相似,提供20款产品,标准齐纳电压范围从5.6V至36V,适用于主要电源线路。此外,该系列还符合AEC-Q101标准—车载电子元件可靠性测试标准。
东芝将继续对适用于车载设备的浪涌保护齐纳二极管产品线进行开发和扩展,以提高车载系统的性能和可靠性。
注:
[1]ECU:电子控制单元
特点
- 高兼容性的小型通用封装
- 低动态电阻
- 针对毫秒级长脉冲的浪涌保护
特点说明
1.高兼容性的小型通用封装
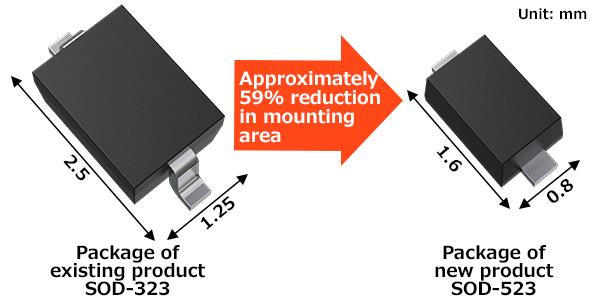
在XCEZ系列中,东芝采用了高兼容性的小型SOD-523封装(1.6×0.8mm),相较于东芝现有XCUZ系列中使用的SOD-323封装(2.5×1.25mm),安装面积减少了约59%,有助于电路板的小型化。
2.低动态电阻
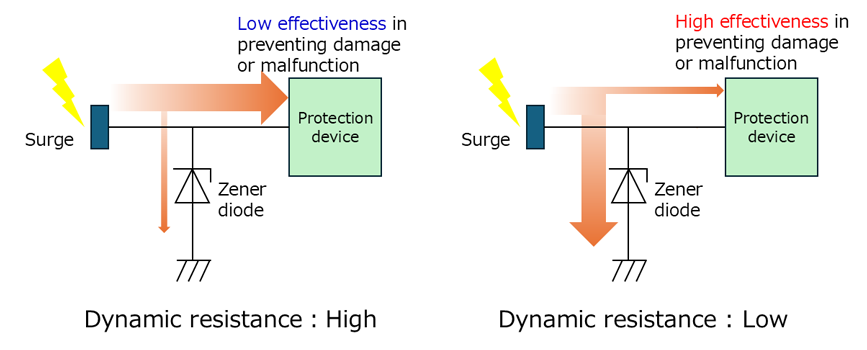
作为一种保护器件,动态电阻是吸收通过电源线路、连接器等侵入的浪涌电压的关键因素。低动态电阻能让浪涌电流更容易流向齐纳二极管。东芝专有的齐纳工艺在反向电压(VR)端呈现出陡峭的ITLP-VTLP曲线,实现了更低的动态电阻,从而能够高效吸收浪涌电压,为器件和电路提供可靠的保护,防止系统发生损坏和故障。
](/content/dam/toshiba-ss-v3/master/en/semiconductor/product/diodes/articles/lineup-expansion-of-surge-protection-zener-diodes-by-adding-20-products-with-small-sod-523-package-for-automotive-equipment_features_4_en.png)
3.针对毫秒级长脉冲的浪涌保护
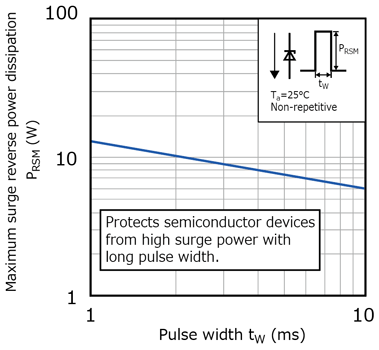
新产品在10ms脉冲宽度下可实现高达6W的允许齐纳浪涌功率(最大值),从而保护半导体器件免受毫秒级长脉宽的冲击,例如高开关浪涌以及接近直流的过电压。
注:
[2]平均窗口:t1=30ns至t2=60ns
应用
- 车载设备(IVI[3]、ADAS[4]、BMS[5]等)
注:
[3]IVI(车载信息娱乐系统):提供信息和娱乐功能的集成系统的通用术语。
[4]ADAS(高级驾驶员辅助系统)
[5]BMS(电池管理系统):用于对充电电池(例如锂离子电池)进行安全控制的系统。
主要规格
(除非另有规定,Ta=25°C)
| 器件型号 | 绝对最大额定值 | 电气特性 | 库存查询与购买 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 静电放电电压VESD[6](kV) | 齐纳电压VZ(V) | 动态电阻RDYN[7](Ω) | 钳位电压VC[7][8](V) |
总电容Ct[9](pF) |
||||||
| 接触 | 空气 | 最小值 | 典型值 | 最大值 | 测试电流IZ(mA) | 典型值 | 典型值 | 典型值 | ||
| XCEZ5V6 | ±30 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 5 | 0.16 | 9.0 | 125 |  |
|
| XCEZ6V2 | ±30 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 5 | 0.21 | 10.0 | 105 |  |
|
| XCEZ6V8 | ±30 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.2 | 5 | 0.27 | 13.0 | 88 |  |
|
| XCEZ7V5 | ±30 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 5 | 0.32 | 14.0 | 78 |  |
|
| XCEZ8V2 | ±30 | 7.7 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 5 | 0.37 | 16.5 | 67 |  |
|
| XCEZ9V1 | ±30 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 5 | 0.44 | 17.0 | 62 |  |
|
| XCEZ10V | ±30 | 9.4 | 10.0 | 10.6 | 5 | 0.52 | 19.0 | 60 |  |
|
| XCEZ11V | ±30 | 10.4 | 11.0 | 11.6 | 5 | 0.60 | 24.0 | 48 |  |
|
| XCEZ12V | ±30 | 11.4 | 12.0 | 12.6 | 5 | 0.70 | 26.0 | 44 |  |
|
| XCEZ13V | ±30 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 14.1 | 5 | 0.80 | 27.0 | 42 |  |
|
| XCEZ15V | ±30 | 13.8 | 15.0 | 15.6 | 5 | 0.60 | 24.0 | 36 |  |
|
| XCEZ16V | ±30 | 15.3 | 16.0 | 17.1 | 5 | 0.50 | 27.0 | 35 |  |
|
| XCEZ18V | ±30 | 16.8 | 18.0 | 19.1 | 5 | 0.40 | 28.5 | 31 |  |
|
| XCEZ20V | ±30 | 18.8 | 20.0 | 21.2 | 5 | 0.35 | 30.5 | 29 |  |
|
| XCEZ22V | ±30 | 20.8 | 22.0 | 23.3 | 5 | 0.40 | 32.0 | 27 |  |
|
| XCEZ24V | ±30 | 22.8 | 24.0 | 25.6 | 5 | 0.60 | 36.5 | 26 |  |
|
| XCEZ27V | ±30 | 25.1 | 27.0 | 28.9 | 2 | 0.90 | 45.0 | 23 |  |
|
| XCEZ30V | ±30 | 28.0 | 30.0 | 32.0 | 2 | 1.25 | 47.5 | 21 |  |
|
| XCEZ33V | ±25 | 31.0 | 33.0 | 35.0 | 2 | 1.80 | 57.0 | 19 |  |
|
| XCEZ36V | ±20 | 34.0 | 36.0 | 38.0 | 2 | 2.60 | 63.0 | 18 |  |
|
注:
[6]符合ISO10605(C=330pF/R=2kΩ)
[7]TLP参数:Z0=50Ω,tp=100ns,tr=300ps,平均窗口t1=30ns至t2=60ns;动态电阻根据ITLP1=16A与ITLP2=30A之间的TLP特性,通过最小二乘法拟合提取。
[8]ITLP=16A
[9]VR=0V,f=1MHz
应用电路示例
![图5:应用电路示例<sup>[10]</sup>](/content/dam/toshiba-ss-v3/master/en/semiconductor/product/diodes/articles/lineup-expansion-of-surge-protection-zener-diodes-by-adding-20-products-with-small-sod-523-package-for-automotive-equipment_features_6_en.png)
注:
[10]此应用电路图为参考示例,请在量产设计时进行充分的评估。此外,其不代表对工业产权的使用许可。
购买、样品、及IC可靠性查询
库存查询与购买
请输入3个以上字符
Through this website you are able to proceed to the website of our distributors ("Third Party Website") which is not under the control of Toshiba Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "Toshiba"). The Third Party Website is made available to you as a convenience only and you agree to use the Third Party Website at your own risk. The link of the Third Party Website does not necessarily imply a recommendation or an endorsement by Toshiba of the Third Party Website. Please be aware that Toshiba is not responsible for any transaction done through the Third Party Website, and such transactions shall be subject to terms and conditions which may be provided in the Third Party Website.
*本文提及的公司名称、产品名称和服务名称可能是其各自公司的商标。
*本文件中所含信息,包括产品价格和产品规格、服务内容及联系方式,仅于公告当日有效,如有更改,恕不另行通知。

