- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
漏极电流ID和IDP(绝对最大额定值)是否随温度变化?
漏极电流的允许范围相对于温度不是恒定不变的,具体取决于环境温度(封装温度)和散热条件(热阻)。
封装的热阻与数据表中所示的最高额定结温与每个产品的允许范围密切相关。
数据表中列出的漏极电流ID・IDP是按25°C的环境温度在理想散热条件下指定的。ID是指在施加直流电时正向漏极电流的最大额定值,而IDP是在指定的脉冲宽度下可以施加的正向漏极电流的额定值。
这些电流被设置为当MOSFET在额定工况下在导通区域(线性区域)内工作时结温不超过Tch(最大值)。
MOSFET在导通区域内温度升高的主要原因是漏极与源极之间的导通电阻RDS(ON)导致的功率损耗PRloss。
例如,求出施加直流电时的正向漏极电流ID。
用以下等式表示由导通电阻RDS(ON)导致的损耗PRloss。
PRloss = RDS(ON) x ID2
假设产品的热阻为Rth(ch-c),则用以下等式表示由损耗产生的热量引起的温升ΔT。
ΔT = PRloss x Rth(ch-c)
结温是通过在MOSFET工作期间将ΔT与的外壳温度TC相加后得出的,因此必须满足以下等式。
Tc+ ΔT < Tch(最大值)
解出ID的上述公式后可得出:可以相同方式考虑IDP。
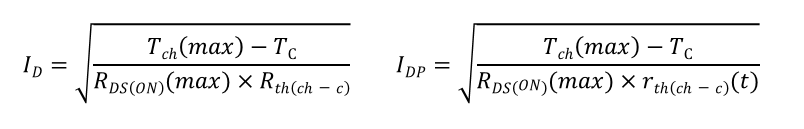

请采纳靠以下文档获取相关信息。

