- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
什么是运算放大器(op-amp)?
运算放大器(op-amp)是放大两个输入之间电压差的集成电路(IC)
由于它是为执行算术运算而开发的,所以如此命名。放大器、缓冲器、比较器、滤波器等可以用简单的外部电路来实现。
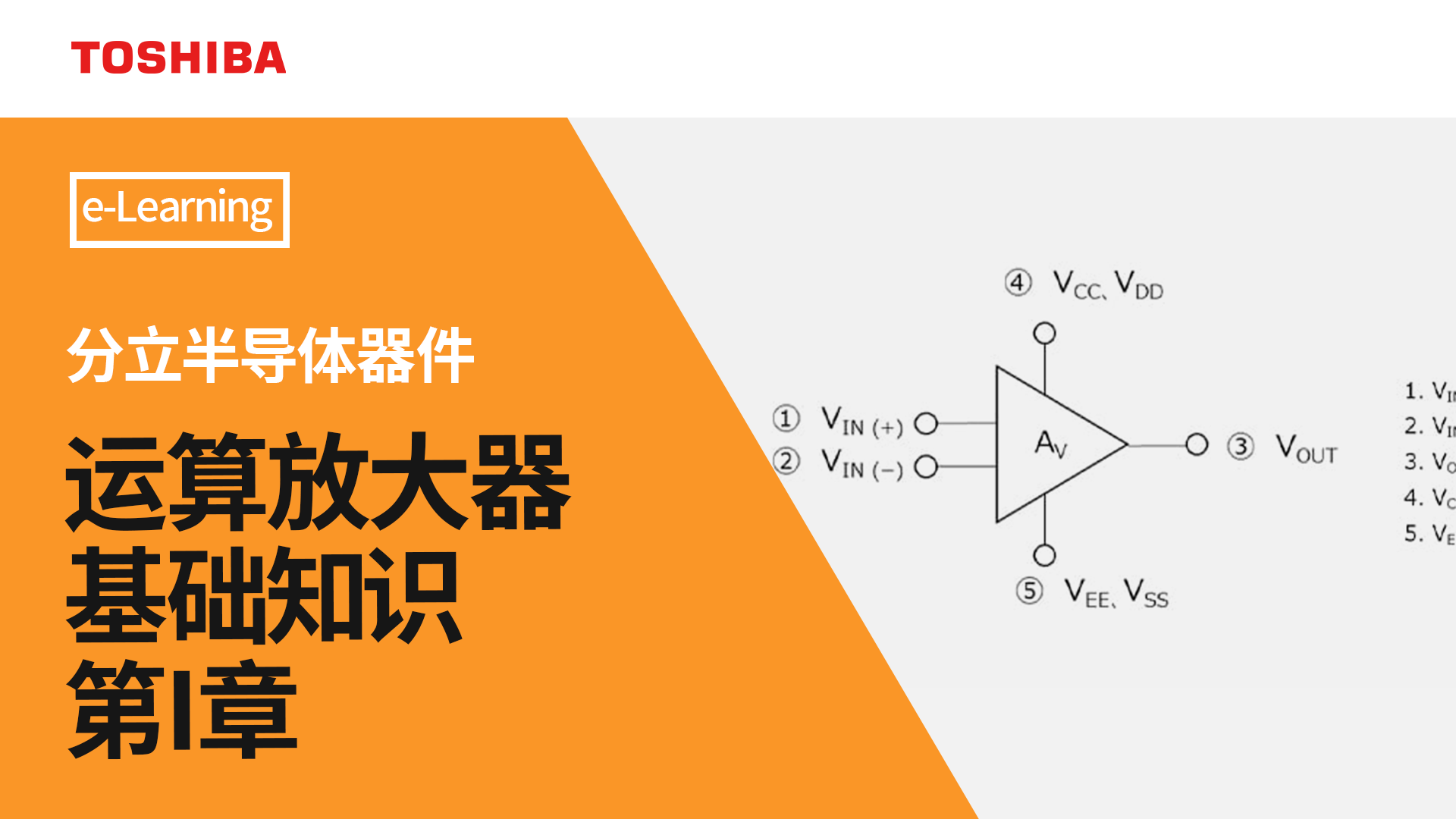
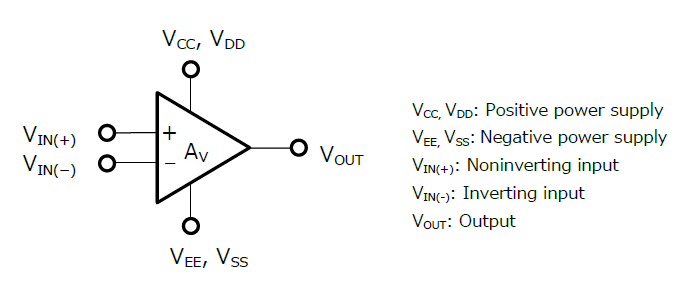
运算放大器有五个端子:正电源、负电源(GND)、同相输入、反相输入和输出。通常,这些端子的命名如下所示。(单电源运算放大器的符号中可能会省略正电源端子和GND端子。)
运算放大器放大同相(IN(+))输入和反相(IN(-))输入之间的电压差。其输出电压按公式1计算,表明输出与VIN(+)同相,与VIN(-)反相。
VOUT=A*( VIN(+)–VIN(-) ) (1)
运算放大器的基本用途就是用作电压放大器或比较器。其还可配置为滤波器、移相器、缓冲器(电压跟随器)等。现今,运算放大器通常用于放大来自各种物联网(IoT)设备和家用电器中传感器的微弱的模拟信号。
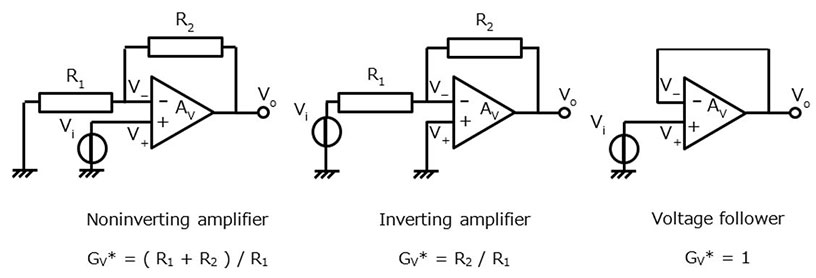
运算放大器通常与负反馈一起使用,以减少增益的乘积变化并扩展带宽。运算放大器的典型应用包括同相放大器、反相放大器和电压跟随器,具体配置方式如下所示:
*:闭环增益
可通过几种方法对运算放大器进行分类。例如,基于以下方式:1)制造工艺(双极型和CMOS);2)电源类型(单电源和双电源);3)输入电路(差分P沟道MOSFET对、差分N沟道MOSFET对、轨到轨输入等);及4)电气特性(低输入补偿、低电流消耗、低噪声等)。另外,运算放大器也可根据其应用进行分类。详细信息,请参考常见问题(FAQ) “有哪些类型的运算放大器可供使用?”
相关链接
以下文档也包含相关信息: