- 型号 & 关键词搜索
- 交叉搜索
- 参数搜索
- 库存查询与购买
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
请输入3个以上字符 Search for multiple part numbers fromhere.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
请输入3个以上字符
什么是偏置电阻内置晶体管(BRT)?
偏置电阻内置晶体管(BRT)亦称为数字晶体管,专门用作开关。BRT是一种双极型晶体管,包含一个串联基极电阻(R1)和一个基极-发射极电阻(R2),从而可以简化板上电路的设计。
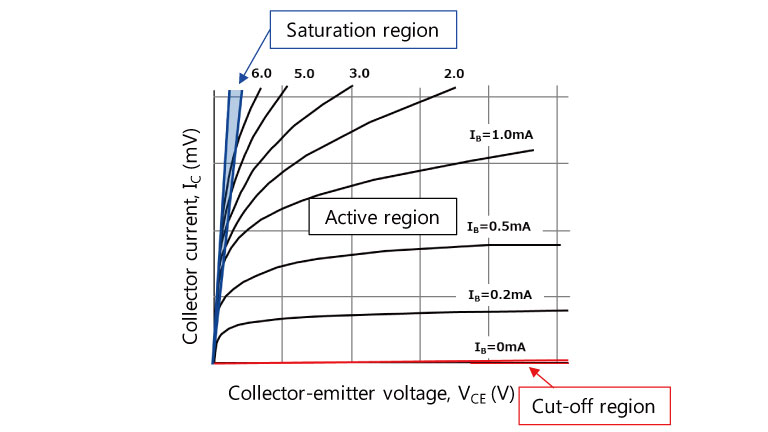
典型的双极晶体管可用作放大器、缓冲器和开关。图2所示的VCE-IC曲线的线性放大区中使用了放大器和缓冲器。相反,主要用作开关的BRT在工作区左侧的区域和工作区下方的区域(分别称为饱和区和截止区)内运行。在饱和区中,集电极-发射极之间的电压降(VCE)最小,从而导致最大集电极电流流动。在截止区中,晶体管完全关断。在截止条件下,只有极小的集电极截止电流(ICEO)可以从集电极流向发射极。
由于内置偏置电阻,BRT导通时在饱和区工作,关断时在截止区工作。
偏置电阻的配置形式如图1所示。R1将施加至B端子的电压转换为电流,以稳定BRT操作,而当BRT关断时,R2作为下拉电阻,从而使基极电压恢复为GND电平。
若无R2,在“关断”状态从输入端流出的泄漏电流或集电极截止电流(ICBO)可能会由于在基极中积累的电荷而导致BRT发生故障。R2可通过使漏电流流向GND来防止故障。