Difference Depending on Metal of Schottky Barrier Diodes (SBDs)
Download "Chapter II : Diodes" (PDF:895KB)
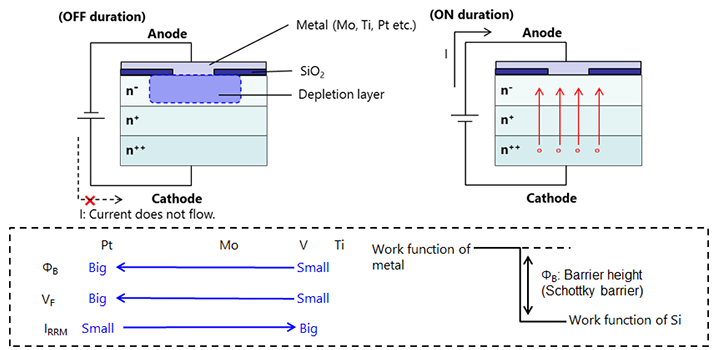
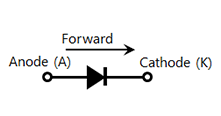
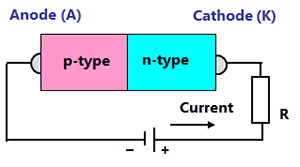
In the case of the SBD, the semiconductor consists of n-type layers, and so the metal acts as the anode of the diode. Likewise, only electrons are carriers, and the SBD becomes a unipolar element just like a MOSFET.
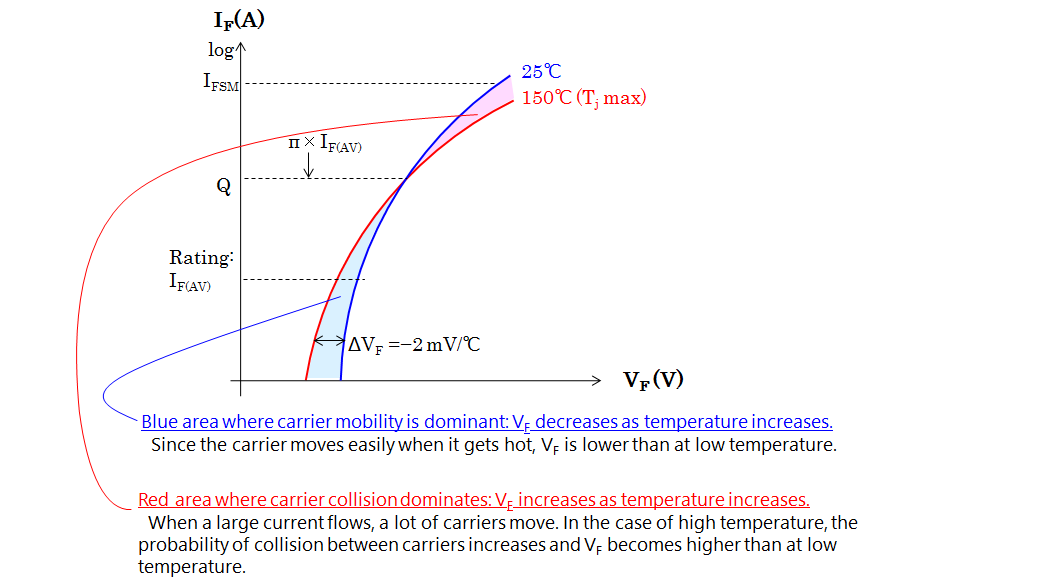
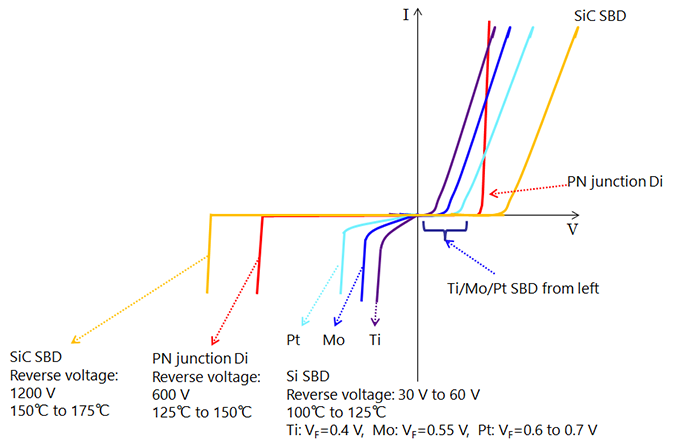
The energy level of silicon differs from metal (energy gap). This energy level differs depending on the metal element. ΦB is the symbol for this difference. Pt (platinum) is a metal with a large energy gap. V (vanadium) or Ti (titanium) are metals with small energy gaps. Adopting a metal with a large ΦB makes leakage current small, but makes forward voltage VF big. For metals with small ΦB, the opposite tendency are obtained.
Chapter II : Diodes
Related information
- Products
- FAQ
A new window will open